Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing and industrial processes. This transformation relies heavily on the use of smart technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, big data, and advanced analytics, to enhance automation, efficiency, and decision-making.
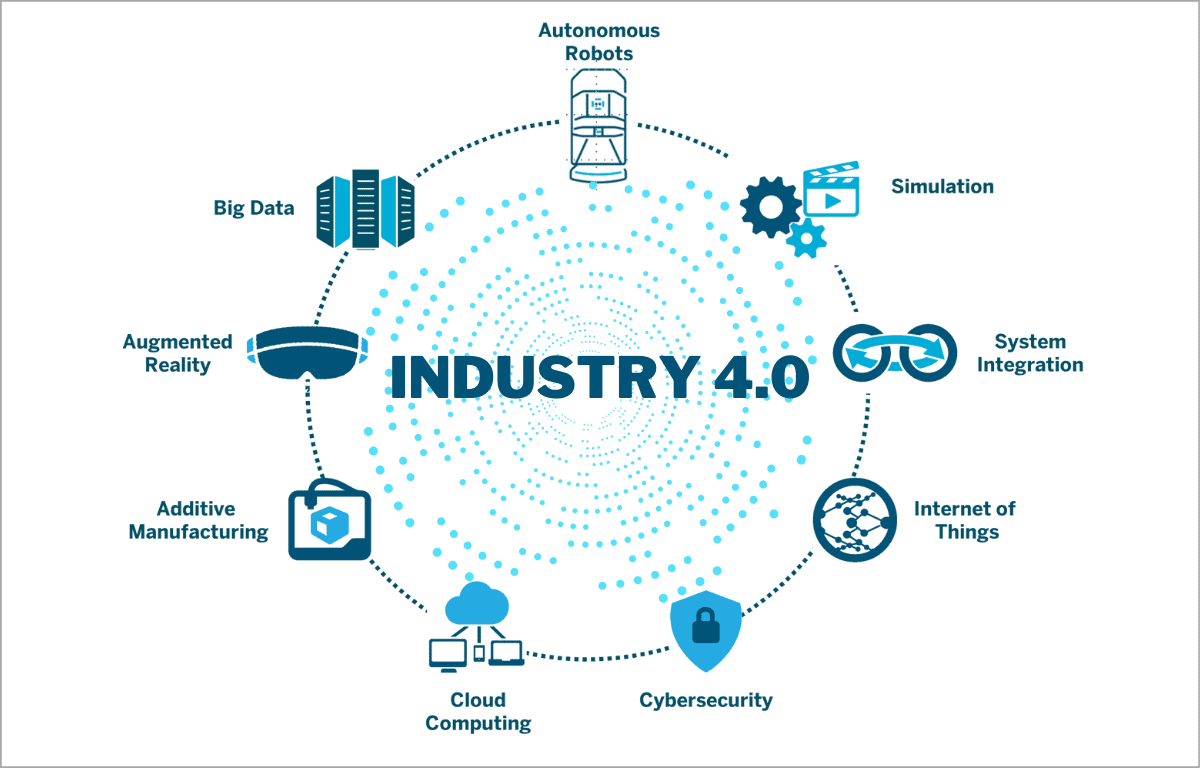
Here are some key components of Industry 4.0:
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS): These systems combine physical processes with digital control systems. For example, machines embedded with sensors and connected to the internet can communicate with other machines, systems, and operators in real time, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and other functions.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices enable machines, products, and systems to communicate and share data over networks, leading to smarter and more efficient manufacturing environments. Sensors and connected devices collect data that can be analyzed to optimize production and logistics.
- Big Data & Analytics: Industry 4.0 generates vast amounts of data that, when analyzed, can provide valuable insights. By leveraging big data and advanced analytics, companies can improve product quality, anticipate maintenance needs, optimize supply chains, and reduce energy consumption.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms analyze data, predict trends, and automate complex tasks. This can lead to smarter decision-making, adaptive manufacturing systems, and even autonomous machines that can make decisions without human intervention.
- Robotics & Automation: Automation through robots and intelligent machines is a hallmark of Industry 4.0. These robots can perform repetitive tasks with greater speed, precision, and flexibility. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans to improve safety and productivity.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing allows manufacturers to create complex parts and products directly from digital models. This reduces waste, speeds up prototyping, and allows for the production of customized or low-volume items.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing enables secure data storage and processing in remote data centers, making information accessible to employees and systems anywhere. It also allows for flexible scaling of resources based on demand.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR are used for tasks such as remote maintenance, training, and product design. Workers can use AR glasses to overlay digital information on physical objects, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing processes data closer to the source (e.g., on factory floors) instead of relying solely on centralized cloud systems. This reduces latency and speeds up decision-making, crucial for real-time manufacturing operations.
Key Benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation and real-time data analysis help optimize processes and minimize downtime.
- Cost Reduction: Predictive maintenance, resource optimization, and reduced waste contribute to significant cost savings.
- Customization: The ability to quickly change production processes allows manufacturers to offer personalized products at scale.
- Improved Product Quality: Continuous monitoring and AI-driven quality control ensure higher product consistency and lower defect rates.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Manufacturing systems can be quickly adapted to different tasks and products, responding to changing market demands.
Challenges:
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity can expose companies to cyber threats.
- Skill Gaps: There’s a need for workers with new skill sets in digital technologies and automation.
- Integration Complexities: Legacy systems may not easily integrate with new Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Data Privacy Concerns: The large volumes of data being generated and processed can raise privacy and regulatory issues.
Industry 4.0 is transforming traditional industries by creating smarter factories, enabling new business models, and enhancing global supply chains. It holds the potential to drastically increase productivity, improve customer satisfaction, and create new opportunities in manufacturing and beyond.